By Jean-Baptiste OUBRIER, AFP
As the global auto sector accelerates the production of electric cars, one British company is hoping to cash in from mining lithium needed to make rechargeable batteries that power the vehicles.
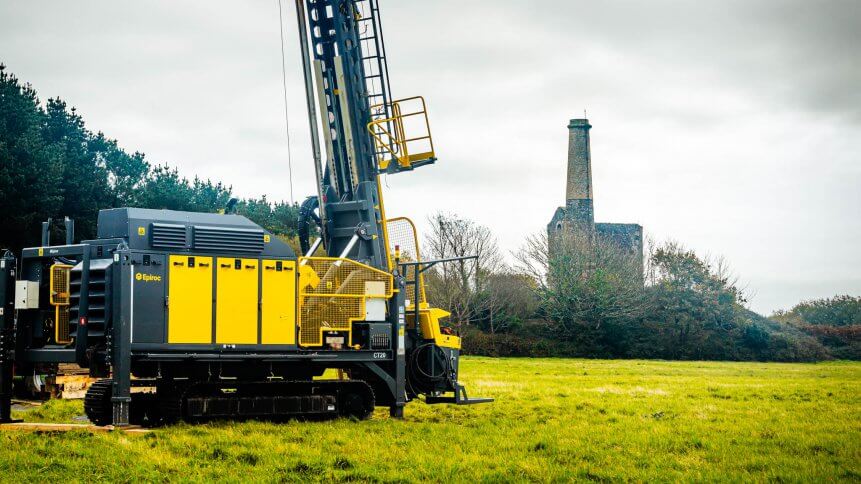
It is five years since former investment banker Jeremy Wrathall launched Cornish Lithium, a company operating in Cornwall, southwest England, which recently hosted the G7 summit.
And while it may be another four years until it begins commercial production of the metal, Wrathall is optimistic that his punt will pay dividends.
“In 2016, I started to think about the electric vehicle revolution and what that would mean for metal demand and I started to think about lithium,” he told AFP in an interview. “A friend of mine mentioned lithium being identified in Cornwall and I just wondered if that was a sort of an unrecognized thing in the UK.”
In fact, lithium was discovered in Cornwall in 1864, while the area is known for its historic copper and tin mining, which dates back 4,000 years and ended at the turn of the century.
“Of course I would like to revive mining in Cornwall but this a commercial project,” insisted Wrathall. “It’s not a mission that drives me to the point to be emotional or romantic.”
‘Encouraging results’
Cornish Lithium is at a testing stage to see if the metal can be produced commercially. “Initial results are encouraging. I’m excited about it,” Wrathall said, whose company has revived a former mine situated away from the area’s picturesque villages and beaches. The mining firm is looking to extract enough lithium from hot water underground to meet at least a “significant proportion” of UK demand for electric cars, while at the same time respecting the environment.
It is mulling the capture of heat from underground to generate clean power, or geothermal energy, that can be used to extract the lithium. Wrathall explained that Cornwall benefitted from having very clean water. “It has a lot of lithium and very little of anything else,” he explained. “When you’re looking for needles in a haystack you want as little hay as possible and more needle and that’s what we’ve got.”
A long journey with lithium for electric cars
The project has been far from easy, from securing drilling rights from landowners to finding the technology to bring water containing lithium to the surface. And the company is facing competition from British Lithium, which is looking to extract the metal from Cornwall’s granite.
British demand for lithium is set to reach 75,000 tonnes by 2035, five years ahead of a UK ban on the sale of high-polluting diesel and petrol vehicles. Lithium is mined mostly in Australia and South America, while China controls the supply chain. And while automakers insist on the environmental benefits of electric vehicles, the bulk of current lithium extraction relies on power from polluting fossil fuels.
In Europe, projects are ongoing for cleaner extraction of the metal in France and Germany. “It’s vitally important that we do get this technology otherwise Europe has got no lithium supply,” Wrathall insisted. It comes as car giants Nissan and Renault recently announced plans for huge plants in England and France to make electric batteries.
The European Commission meanwhile wants to end the sale of new petrol and diesel cars by 2035, under a massive plan to fight climate change unveiled last week. “Europe from a strategic point of view should be looking at securing its own supply of lithium,” said Alex Keynes at Brussels-based lobby group Transport & Environment.
“Our view is that medium-to-long term the majority of materials including lithium should come from efficient and clean recycling,” he told AFP.
© Agence France-Presse