Is Michigan becoming a hub for self-driving vehicle makers?
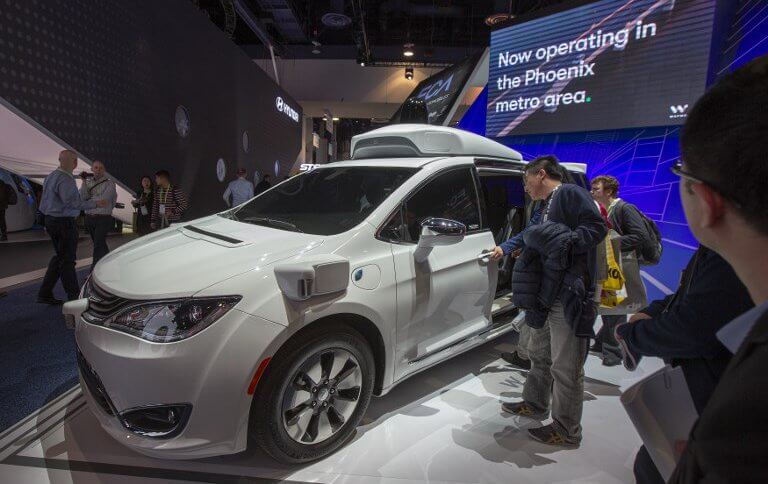

Self-driving car leaders Waymo and Magna are partnering to build a car factory that will be dedicated to the mass production of Level Four (L4) autonomous vehicles, in southeast Michigan in the United States.
The factory will be home to the manufacturing of thousands of vehicles, including the production of autonomous versions of the all-electric Jaguar I-PACE and Chrysler Pacifica Hybrid minivan.
We're getting started on the world’s first factory that is 100%-dedicated to the mass production of L4 autonomous vehicles, creating hundreds of jobs in Michigan. @MEDC #PureMichigan https://t.co/dWuRyjfYtp
— John Krafcik (@johnkrafcik) January 22, 2019
In a blog post, Waymo announced that the Michigan Economic Development Corporation (MEDC) voted to approve the company’s efforts to establish a manufacturing presence.
Talking to Techcrunch, the company expects to create up to 400 new jobs. It’s reported that up to 20,000 modified I-Pace vehicles will join the company’s driver-less ride-hailing service in the first two years of its operation. There is also a deal with Fiat Chrysler Automobiles (FCA) for up to 62,000 modified minivans.
MEDC CEO Jeff Mason said the move emphasizes the significance of Michigan in the development of self-driving vehicles: “It shows Michigan is the place where we are able to integrate this technology into the vehicles […] it shows Michigan is the place in North America where companies are coming to bring this technology to life,” he said.
Waymo already conducts vehicle tests in the Great Lakes State at a 53,000 sq ft self-driving technology center in Novi. Its local engineers have been working on many different parts of its technology, and the outfitting of its fleet of minivans is already underway with the company’s built suite of sensors.
News of the company’s manufacturing expansions plans has already brought calls for engineers, operations experts and fleet coordinators to join their team in order to help assemble and deploy its self-driving cars.
Laying a foundation for a scalable yet robust vehicle integration plan starts in Michigan, and is probably an indication that its aspirations for wide-ranging commercial operations are now underway in earnest, following the launch of a limited commercial ‘self-driving’ ride-hailing service in the Phoenix area, called Waymo One.
YOU MIGHT LIKE

Are self-driving cars the offices of the future?
Currently, Waymo’s service still requires a trained test driver behind the wheel and the safety driver will eventually be removed from the vehicle this year, as the service gradually opens up to more people.
L4 autonomous driving does get categorized as ‘fully autonomous’, and vehicles are designed to perform all safety-critical driving functions and monitor roadway conditions for an entire trip. However, the categorization is so far limited to the ‘operational design domain’ of the vehicle, which means it does not cover every driving scenario.